What is membrane electrode assemblies?
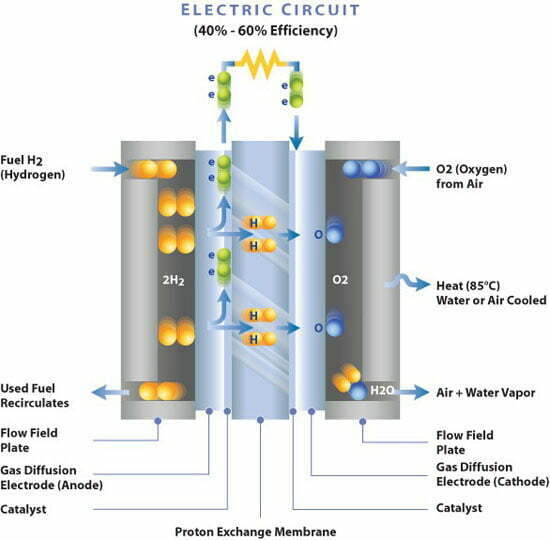
The membrane electrode assemblies(MEA) is the most central component of the hydrogen fuel cell. And is the core site for several material transport and electrochemical reactions.
Its preparation technology not only directly affects the performance of the battery. But also is crucial to reduce the cost of the battery and improve the specific power and specific energy of the battery. It is imaginatively called the “heart” of the fuel cell.
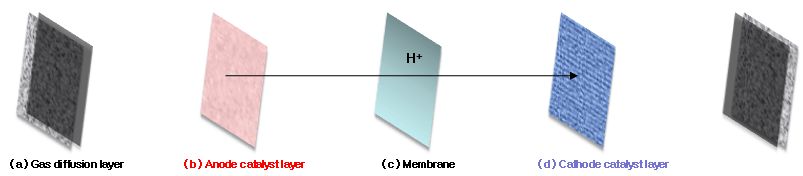
The membrane electrode assemblies, on the other hand, is mainly composed of three parts: catalyst, proton exchange membrane and gas diffusion layer. they are pressed into a three-in-one assembly at the corresponding temperature and pressure.
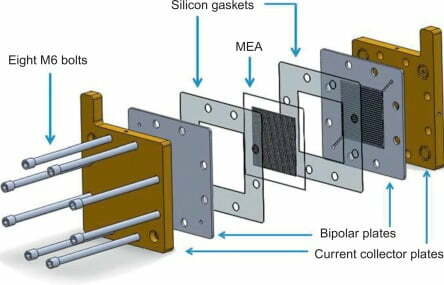
It undertakes all the electrochemical reactions of fuel cells and the conduction of electrons, protons, gases and water. And determines the upper limit of the performance, lifetime and cost of electric stacks. High-performance, low platinum loading, low-cost and long-life membrane electrodes are of great importance to accelerate the commercialization of hydrogen fuel cells.
What are the type of membrane electrode assemblies?
The first generation of membrane electrode assemblies by hot pressing (GDE). It refers to coating the catalyst on the gas diffusion layer and later combining the gas diffusion electrode and the proton exchange membrane by hot pressing. The overall performance of this method is not high and largely eliminated.
The second generation of CCM membrane electrode assemblies. It refers to the direct coating of slurry consisting of catalyst, sulfonic acid resin. And appropriate dispersant onto both sides of the proton exchange membrane using roll-to-roll direct coating, screen printing, spraying, etc. This method improves catalyst utilization (less than 0.4 mg/cm2) and durability. And is currently the most commercially available and has mass-produced.
The third generation of ordered membrane electrode assemblies. It refers to the preparation of Pt catalysts onto ordered nanostructures to make the electrodes. In an ordered structure and obtain a strong and complete catalytic layer.
And this method further improves the fuel cell performance and reduces the catalyst platinum loading (≈0.1mg/cm2). which is the current hot spot for membrane electrode manufacturing research. But it is still in the R&D trial stage and only a small number of companies have achieved mass production, such as 3M.